📋 Table of Contents
Microsoft Excel’s revolutionary new COPILOT function transforms spreadsheet work by bringing artificial intelligence directly into formulas. Moreover, this groundbreaking feature lets you use natural language prompts within cells, fundamentally changing how we interact with data. Instead of complex formulas, you can simply type what you need in plain English and let AI handle the heavy lifting.
As Excel continues evolving with AI integration, the copilot function excel represents a significant leap forward in spreadsheet automation. Therefore, understanding how to leverage this powerful tool gives you a competitive edge in data analysis, text processing, and content generation tasks that previously required extensive manual effort.
What is the COPILOT Function in Excel?
The =COPILOT() function represents Excel’s first native integration of large language model capabilities directly into the calculation engine. According to Microsoft’s official documentation, this function allows users to leverage artificial intelligence by providing prompts and grid references to generate AI-powered responses based on the GPT-4.1-mini model.
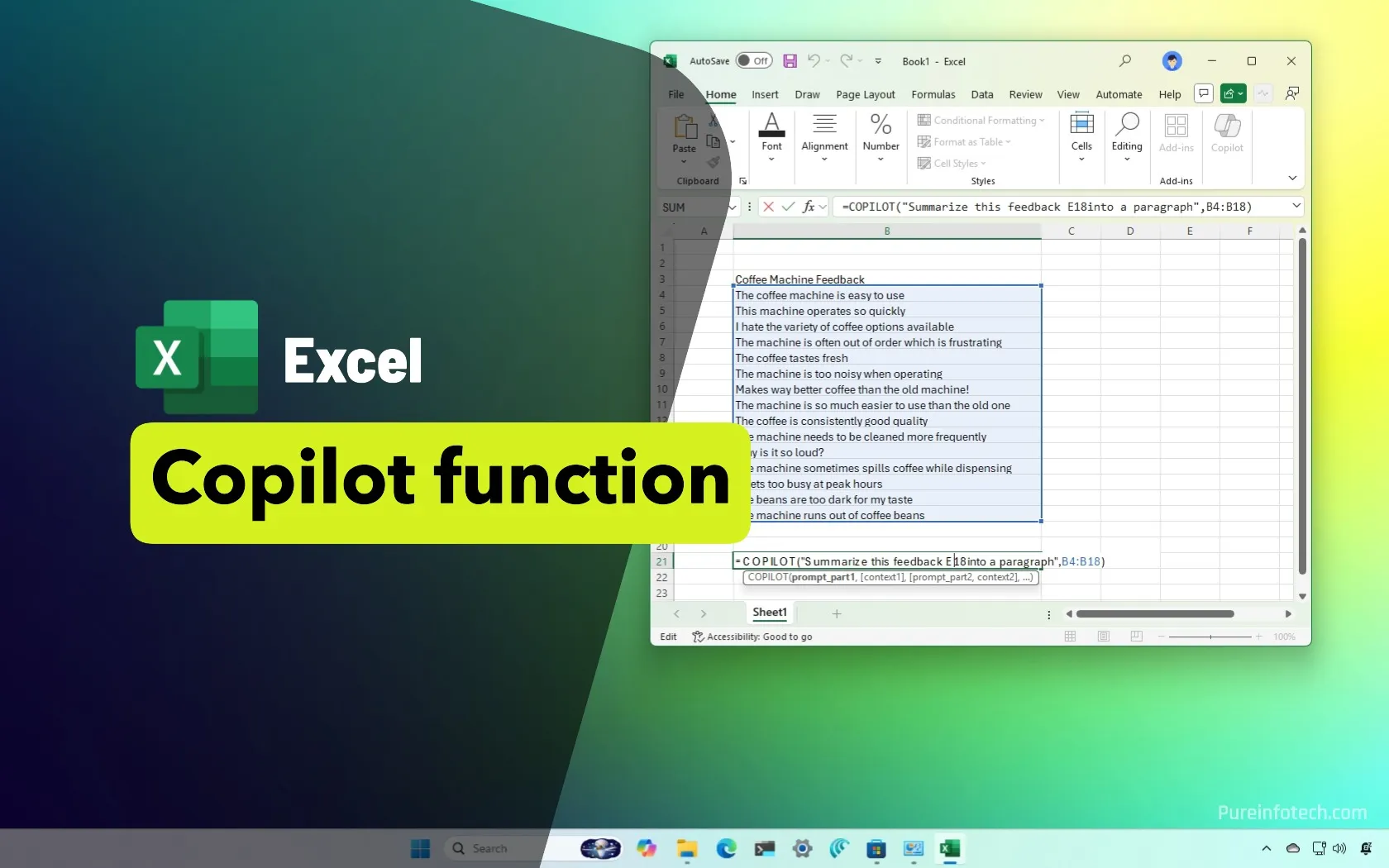
Key Differences from Regular Excel Copilot
Understanding the distinction between the copilot function in excel and the regular Copilot feature is crucial for effective usage. Based on insights from Kenji Explains’ comprehensive tutorial, the function operates independently of AutoSave requirements and integrates seamlessly with Excel’s calculation system, whereas the chat-based Copilot requires specific file conditions and table formatting.
COPILOT Function Advantages:
- Works directly within cells like traditional formulas
- No AutoSave requirement – functions in offline mode
- Integrates with Excel’s calculation engine for dynamic updates
- Supports array spilling for multi-result outputs
- Compatible with other Excel functions through nesting
- Processes natural language instructions efficiently
| Feature | COPILOT Function | Regular Copilot |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inside cells as formula | Side panel interface |
| AutoSave | Not required | Must be enabled |
| Data Format | Any cell range | Formatted as table |
| Integration | Native formula support | Separate interface |
Licensing Requirements & Access for Copilot Function in Excel
The COPILOT function excel requires a Microsoft 365 Copilot license and is currently in Beta status. According to Microsoft’s official support documentation, this function is only available to users on the Beta Channel through the Microsoft 365 Insider program, with access restricted to commercial customers possessing valid Copilot subscriptions.
Important License Note: If you attempt to use the COPILOT function without proper licensing, Excel will display a “BLOCKED” error message. Personal Microsoft 365 subscriptions (Family/Personal) do not support this functionality, regardless of subscription status, as confirmed by Pureinfotech’s comprehensive guide.
System Requirements & Availability
The function is currently rolling out to Beta Channel users with specific version requirements. Additionally, geographic availability varies, with most regions supported except for certain countries where AI services may be restricted, as noted in Microsoft’s Tech Community announcement.
| Platform | Minimum Version | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Excel for Windows | Version 2509 (Build 19212.20000) | Beta Channel |
| Excel for Mac | Version 16.101 (Build 25081334) | Beta Channel |
| Excel for Web | Rolling out soon | Frontier Program |
How to Check Your License Status
To determine if you have access to the copilot() function excel, navigate to your Microsoft 365 admin center and check your subscription details. Furthermore, you can test access by typing =COPILOT( in any Excel cell – if the function appears in the autocomplete dropdown, you have proper licensing as demonstrated in Kevin Stratvert’s detailed walkthrough.
🚀 Level Up Your Career with Excel & DataCamp!
DataCamp Flash Sale: 50% OFF until September 25th!
Learn Power BI, SQL & Data Skills trusted by top companies.
550+ interactive courses & industry-recognized certifications.
Offer valid September 1st (11:59am EST) – September 25th (23:59 EST).
Getting Started with Copilot function in Excel: Setup & Basic Usage
Once you have proper licensing, getting started with the copilot function in excel is straightforward. Based on demonstrations from Microsoft’s official introduction video, the function integrates seamlessly into Excel’s existing formula framework, making it accessible to anyone familiar with basic Excel operations.

First Steps with COPILOT Function:
- Open Excel and create a new workbook or open existing data
- Click on any cell where you want the AI-generated results to appear
- Type =COPILOT( and Excel will show the function signature
- Enter your natural language prompt in quotation marks
- Optionally add context data by referencing cell ranges
- Close parentheses and press Enter to execute the function
Your First COPILOT Function Example
Let’s start with a simple example that demonstrates the power of natural language processing in Excel. This basic usage shows how the copilot function excel can generate information without requiring any existing data, as illustrated in multiple expert tutorials from Excel Campus’s 17 practical examples.
Example: =COPILOT(“Give me 5 popular programming languages”)
This simple formula will return a list of programming languages directly in your spreadsheet, demonstrating the function’s ability to generate content based on its training data.
Function Syntax & Parameters
The copilot() function excel follows a specific syntax structure that supports both simple prompts and complex data analysis tasks. According to Microsoft’s official documentation, the function constructs prompts by combining all prompt_part and context arguments to create comprehensive AI instructions.
Complete Function Syntax
The official syntax for the COPILOT function is: =COPILOT(prompt_part1, [context1], [prompt_part2], [context2], ...)
| Parameter | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| prompt_part1 | Yes | Natural language instruction | “Summarize this data” |
| context1 | No | Cell range for AI to analyze | A1:A10 |
| prompt_part2 | No | Additional instructions | “into categories” |
| context2 | No | Additional data reference | B1:B5 |
Advanced Parameter Usage Patterns
The copilot function in excel supports multiple prompt and context pairs, enabling sophisticated data analysis workflows. As demonstrated in Microsoft’s technical blog post, this flexibility allows you to provide comprehensive instructions while referencing multiple data sources within a single formula.
Pro Tip: Use array inputs when processing multiple rows or columns simultaneously. According to Microsoft’s usage guidelines, this approach counts as a single API call rather than multiple individual calls, helping you stay within the 100 calculations per 10 minutes limit while processing larger datasets efficiently.
Practical Examples & Use Cases for New Excel Copilot() function
Real-world applications of the copilot function excel span across industries and use cases. These practical examples demonstrate how AI integration transforms routine spreadsheet tasks into automated, intelligent processes, as showcased in comprehensive tutorials from Excel Campus and Kevin Stratvert’s channel.
Data Classification and Sentiment Analysis
One of the most powerful applications involves analyzing customer feedback, survey responses, or product reviews. The copilot function in excel can simultaneously categorize content and assess sentiment, providing comprehensive insights in a single operation, as demonstrated in Kenji Explains’ practical tutorial.
Example: =COPILOT(“Analyze these customer reviews”, A2:A20, “return sentiment and category”, B1:C1)
This formula analyzes customer reviews in column A and returns both sentiment scores and categories based on your predefined headers in row 1.
Text Extraction and Data Parsing
Complex text parsing tasks become simple with natural language instructions. Whether you’re extracting names from addresses, parsing product information, or standardizing data formats, the AI understands context and handles variations automatically, as shown in multiple use cases from Excel Campus’s comprehensive guide.
Data Parsing Use Cases:
- Extract first names, last names, and cities from mixed address formats
- Parse product orders containing size, color, and quantity information
- Standardize company names with variations and abbreviations
- Convert mixed date formats into consistent YYYY-MM-DD format
- Categorize expense descriptions into predefined budget categories
Content Generation and Planning
Beyond data analysis, the copilot function excel excels at generating structured content for planning and creative tasks. From meal planning to itinerary creation, AI can generate comprehensive solutions based on your specific requirements and constraints, as demonstrated in Kevin Stratvert’s itinerary planning example.
Advanced Techniques & Best Practices
Mastering the copilot function excel requires understanding advanced techniques that optimize performance, accuracy, and efficiency. According to Microsoft’s official guidelines and expert recommendations from Excel Campus, these strategies help you maximize the function’s potential while working within system limitations and usage quotas.
Optimizing for Usage Limits
The function currently supports 100 calls per 10 minutes according to Microsoft’s official documentation. Therefore, strategic planning helps you accomplish more within these constraints while maintaining optimal performance.
Efficiency Best Practices:
- Process entire ranges instead of individual cells to minimize API calls
- Use UNIQUE function to process only distinct values when appropriate
- Combine multiple operations in single prompts rather than separate functions
- Reference header rows to guide output structure and column naming
- Validate critical outputs as AI can occasionally produce unexpected results
Integration with Other Excel Functions
The copilot() function excel works seamlessly with Excel’s existing function library, enabling sophisticated workflows that combine AI processing with traditional calculations and data manipulation. However, Microsoft specifically recommends using native Excel functions like XLOOKUP for data lookup operations rather than COPILOT.
Working with Spill Ranges and Dynamic Arrays
Understanding how the COPILOT function interacts with Excel’s dynamic array features enables more sophisticated data processing workflows. According to Microsoft’s documentation, when the function returns multiple results, Excel automatically spills the output across adjacent cells, creating dynamic ranges that update automatically.
Limitations & Considerations
While the copilot function in excel represents a significant advancement in spreadsheet AI, understanding its current limitations helps set appropriate expectations and guides effective implementation strategies. Based on Microsoft’s official documentation and insights from CollabSummit’s technical analysis, several important constraints affect functionality.
Current Technical Limitations
The function operates within specific constraints that affect its performance and applicability. Microsoft’s official documentation clearly outlines these limitations to help users design workflows that work reliably within the system’s current capabilities.
| Limitation | Impact | Workaround |
|---|---|---|
| No web access | Cannot fetch live data | Import data first, then process |
| Usage quotas | 100 calls per 10 minutes | Batch processing, use arrays |
| Date formatting | Returns text, not date serials | Convert using DATEVALUE function |
| Confidential workbooks | Cannot calculate in protected files | Remove sensitivity labels or use alternatives |
When NOT to Use COPILOT Function
Microsoft explicitly states in their official documentation that “COPILOT uses AI and can give incorrect responses.” Therefore, understanding inappropriate use cases is crucial for responsible implementation.
Avoid COPILOT for Numerical Calculations: According to Microsoft’s guidelines, use native Excel formulas (SUM, AVERAGE, IF) for any task requiring accuracy or reproducibility, as AI-generated mathematical results may be inconsistent or incorrect.
Privacy and Security Considerations
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, “Your prompts and data supplied as context will not be used to train AI models.” However, the function requires an active internet connection to access Azure-hosted AI models, so organizations should consider their data governance policies when using this functionality with sensitive information.
📈 Master Excel & Data Analytics
Join 10M+ learners on DataCamp. Learn at your own pace, from beginner to pro.
Your career growth starts here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a Microsoft 365 Copilot license to use the COPILOT function?
Yes, according to Microsoft’s official documentation, the COPILOT function excel requires a Copilot subscription and Beta Channel access through the Microsoft 365 Insider program. Without proper licensing, Excel will display a “BLOCKED” error when you attempt to use the function.
How is the COPILOT function different from regular Excel Copilot?
The copilot function in excel works directly within cells as a formula, requires no AutoSave, and processes any cell range. Regular Copilot operates through a side panel, requires AutoSave enabled, and works only with properly formatted tables, as explained in Kenji Explains’ tutorial.
What are the usage limits for the COPILOT function?
According to Microsoft’s documentation, current limits include 100 calculations per 10 minutes. However, processing entire ranges counts as single calls, so batch operations help you stay within limits while handling larger datasets efficiently.
Can the COPILOT function access real-time web data?
No, Microsoft’s documentation states the function cannot directly access live web data or internal business documents. The model’s knowledge is limited to information before June 2024, and you must first import external data into your workbook before processing it with COPILOT.
Should I use COPILOT for mathematical calculations?
No, Microsoft explicitly recommends using native Excel formulas (SUM, AVERAGE, IF) for numerical calculations requiring accuracy or reproducibility, as the AI can provide incorrect mathematical results.
What should I do if the COPILOT function returns unexpected results?
Since Microsoft warns that “COPILOT uses AI and can give incorrect responses,” always validate critical results. Try refining your prompts with more specific instructions, provide examples of desired output format, or break complex requests into smaller operations for better accuracy, as suggested by Excel Campus experts.
🚀 Ready to Transform Your Excel Workflows?
The COPILOT function represents the future of spreadsheet automation, bringing AI-powered data processing directly into Excel’s familiar formula environment. Based on comprehensive testing by Excel experts and Microsoft’s official guidance, this function excels at semantic tasks while maintaining integration with Excel’s existing capabilities.
Start exploring these capabilities today and discover how natural language processing can streamline your data analysis tasks.

